Joseph R. Anticaglia, MD
Medical Advisory Board
Jared Kushner, the 42 year old former White House senior advisor, and son-in-law of ex-President Donald J. Trump, revealed in his 2022 book “Breaking History” that he had been treated for thyroid cancer. He was diagnosed as having thyroid cancer in October 2019 when a biopsy performed at Walter Reed Hospital tested positive for thyroid cancer.
His first surgery was performed in 2019 at Columbia Presbyterian Hospital, in New York on the Friday before Thanksgiving which involved the removal of a substantial part of the thyroid, partial thyroidectomy. He underwent a second surgical procedure on the thyroid gland in 2022, in Rochester, Minnesota.
The American Cancer Society estimates that in 2022 there were approximately 43,800 new cases of thyroid cancer in the United States. Cancer is more prevalent in women by about a 3 to 1 ratio (31,940 in women and 11,860 in men). Every year about 950 men, and 1,100 women die from this cancer.
Thyroid cancer is a disease in which abnormal, malignant (cancer) cells divide, and multiply without control in thyroid tissue. The cancer cells can invade nearby tissues, or invade other parts of the body through the blood, and lymph system.
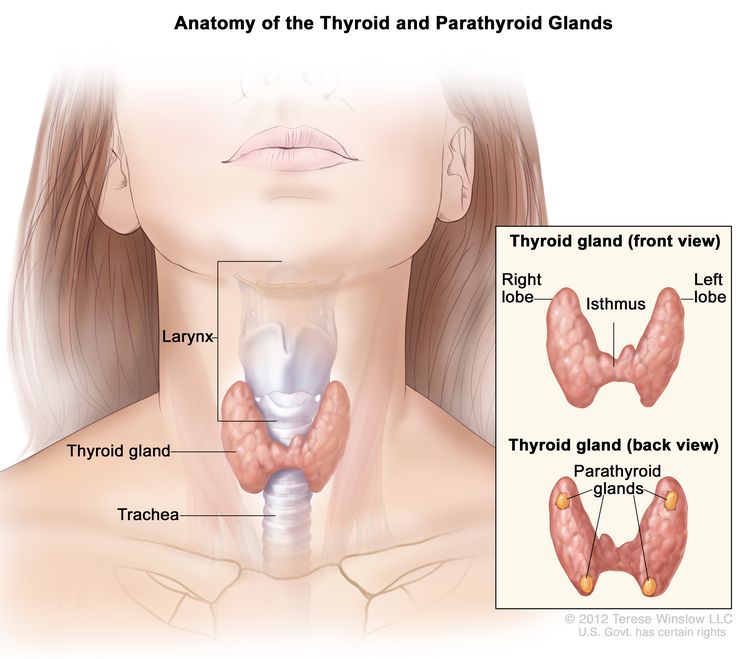
The thyroid gland is a butterfly shaped endocrine gland located in the neck below the Adam’s apple and in front of the windpipe It consists of right and left thyroid lobes joined together by a narrow strip of thyroid tissue called the isthmus.
Two Main Thyroid Cell Types
- Follicular cells use iodine from the blood to make thyroid hormone which help regulate the body’s metabolism.
- C cells are parafollicular cells that make the hormone calcitonin which help regulate how the body uses calcium.
Four Major Types of Thyroid Cancers
When thyroid cells mutate, they undergo changes to their DNA’ s instruction manual. These malignant, cancerous cells instead of dying and being replaced by other healthy cells, are programmed to grow, multiply, and form tumors.
The staging of the cancer, and the identification of the cell types indicates the seriousness of the cancer, and influence the treatment decisions, and outcomes
Thyroid cancers can be classified as differentiated cancers in which the cells look more like normal cells, and tend to grow, and spread more slowly. For example, papillary thyroid cancer. is the most common major thyroid cancer, and the least aggressive thyroid cancer. Isaac Asimov most likely had this type of cancer, and Rod Stewart was diagnosed with papillary cancer.
In comparison, poorly differentiated or undifferentiated cancer cells, for instance, anaplastic thyroid cancer cells poorly resemble normal cells. These cancer cells ruin the features, and vital functions of normal cells. This cancer grows, and spreads quickly. Anaplastic cancer is the least common major thyroid cancer, and the most aggressive thyroid cancer. Former Chief Justice William Rehnquist was suspected of having this type of malignancy.
- Papillary Thyroid Cancer is the most common type of thyroid cancer making up about 80% of all thyroid cancer cases. This differentiated cancer tends to grow slowly, often involves one lobe of the thyroid, can spread to lymph nodes, and are seldom fatal. It generally affects people 30 to 50 years of age. Patients with papillary cancer have an excellent prognosis.
- Follicular Thyroid Cancer is the second most common type of thyroid cancer. It makes up 10 to 15% of the cases, and generally affects individuals 50 years of age or older. These differentiated cancers tend to be more aggressive than papillary cancers spreading to other parts of the body like the lungs, and bones but not to the lymph glands.
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer arises from the C cells in the thyroid gland and accounts for about 2% of all thyroid cancers. It tends to spread more quickly than papillary or follicular thyroid cancer. A faulty gene may account for a significant family history of this type of thyroid cancer
- Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer is an undifferentiated, aggressive cancer that grows, and spreads quickly to surrounding tissue and to distant parts of the body. It accounts for about 2% of thyroid cancers.
When reporters asked Mr. Kushner to reveal more details about his cancer, he said, “It’s none of your business.” And indeed, it is none of our business, but we do wish he, and others dealing with thyroid cancer have the type with the most favorable outcome.
Reference
- Joseph R. Anticaglia, MD; Thyroid Gland What Is It? What Does It Do? The Pituitary—Thyroid Connection; Doctor’s Column HC Smart February 2023
- Paul A. Fitzgerald, MD; Thyroid Cancers; Current Diagnosis and Treatment. 2018
- American Cancer Society; What Is Thyroid Cancer? March 14, 2019
- CDC; Thyroid Cancer; March 8, 2021
- Cleveland Clinic, Thyroid Gland 10/24/2022.
- Fany Moreno et al; Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma with unusual long term survival; BMC February I, 2022
Glossary
Cancer is a diseases caused by abnormal cells which divide uncontrollably. The cancer cells can invade nearby tissues, or metastasize, spread to other parts of the body via blood and lymph systems.
Papillary cancer, also called papillary carcinomas or papillary adenocarcinomas.
Follicular cancer, also called follicular carcinoma or follicular adenocarcinoma.
Anaplastic thyroid cancer, also called poorly differentiated, or undifferentiated, is an aggressive cancer.
C cells are parafollicular cells that make the hormone calcitonin.
Lymphocytes are immune system white blood cells found less commonly in the thyroid gland.
This article is intended solely as a learning experience. Please consult your physician for diagnostic and treatment options.

